Golang program for implementation of Random Maze Generator
A maze can be generated by starting with a predetermined arrangement of cells with wall sites between them. This predetermined arrangement can be considered as a connected graph with the edges representing possible wall sites and the nodes representing cells. The purpose of the maze generation algorithm can then be considered to be making a sub-graph in which it is challenging to find a route between two particular nodes.
Example
package main
import (
"bytes"
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time"
)
type Maze struct {
c,h,v []byte
cell,hor,ver [][]byte
}
func DrawMaze(rows, cols int) *Maze {
c := make([]byte, rows*cols)
h := bytes.Repeat([]byte{'-'}, rows*cols)
v := bytes.Repeat([]byte{'|'}, rows*cols)
cell := make([][]byte, rows)
hor := make([][]byte, rows)
ver := make([][]byte, rows)
for i := range hor {
cell[i] = c[i*cols : (i+1)*cols]
hor[i] = h[i*cols : (i+1)*cols]
ver[i] = v[i*cols : (i+1)*cols]
}
return &Maze{c, h, v, cell, hor, ver}
}
func (m *Maze) String() string {
hWall := []byte("+---")
hOpen := []byte("+ ")
vWall := []byte("| ")
vOpen := []byte(" ")
rightCorner := []byte("+\n")
rightWall := []byte("|\n")
var b []byte
// for all rows
for r, hw := range m.hor {
// draw h walls
for _, h := range hw {
if h == '-' || r == 0 {
b = append(b, hWall...)
} else {
b = append(b, hOpen...)
}
}
b = append(b, rightCorner...)
// draw v walls
for c, vw := range m.ver[r] {
if vw == '|' || c == 0 {
b = append(b, vWall...)
} else {
b = append(b, vOpen...)
}
// draw cell contents
if m.cell[r][c] != 0 {
b[len(b)-2] = m.cell[r][c]
}
}
b = append(b, rightWall...)
}
// draw bottom edge of maze
for _ = range m.hor[0] {
b = append(b, hWall...)
}
b = append(b, rightCorner...)
return string(b)
}
func (m *Maze) generator() {
// Allocate the maze with recursive method
m.recursion(rand.Intn(len(m.cell)), rand.Intn(len(m.cell[0])))
}
const (
up = iota
down
right
left
)
func (m *Maze) recursion(row, col int) {
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
m.cell[row][col] = ' '
for _, wall := range rand.Perm(4) {
switch wall {
// Whether cells up is out or not
case up:
if row > 0 && m.cell[row-1][col] == 0 {
m.hor[row][col] = 0
m.recursion(row-1, col)
}
// Whether cells down is out or not
case down:
if row < len(m.cell)-1 && m.cell[row+1][col] == 0 {
m.hor[row+1][col] = 0
m.recursion(row+1, col)
}
// Whether cells left is out or not
case left:
if col > 0 && m.cell[row][col-1] == 0 {
m.ver[row][col] = 0
m.recursion(row, col-1)
}
// Whether cells to the right is out or not
case right:
if col < len(m.cell[0])-1 && m.cell[row][col+1] == 0 {
m.ver[row][col+1] = 0
m.recursion(row, col+1)
}
}
}
}
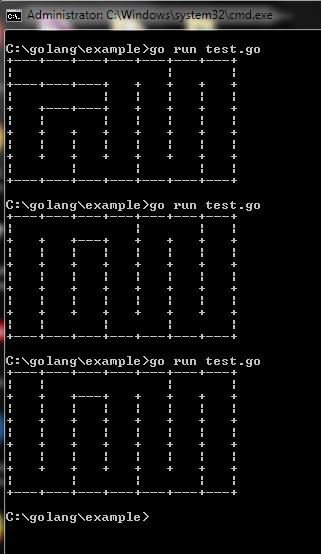
func main() {
d := DrawMaze(5,7)
d.generator()
fmt.Print(d)
}
Most Helpful This Week
Go program to find Name Server (NS) record of a domain
Interface Accepting Address of the Variable in Golang
This sample program demonstrates how to decode a JSON string.
Read and Write Fibonacci series to Channel in Golang
How to copy one slice items into another slice in Golang?
How do you write multi-line strings in Go?
